Introduction of Teams
international Robotour, teams from five countries
When we decided that the next country hosting the Robotour contest will be Austria, we were a little bit afraid. There was no Austrian team in Bratislava last year. But now it looks more promising — not only there are two new teams from Austria, there is also one new team from Poland and one from Slovenia.
The current number of teams is 15. This is surely not the final count, because,
as every year, not all the teams manage to finish their robot in time. You can look
forward to see experienced „troupers” as well as „newbies”, approximately in 1:1 ratio.
Troupers
Teams like ARBot, Eduro Team, Radioklub Písek, Roboauto (2x), Short Circuits
Prague and Smelý Zajko you could have already seen on Robotour contest before, mostly
many times. That does not necessarily mean that the robots will be exactly the
same with the same brains…
ARBot
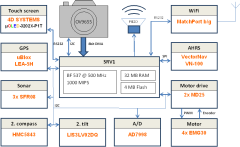
ARBot is a small robotic vehicle with dimensions 28x28x50 cm. It is based on
boogie 4WD1 from Lynxmotion with 4 motors EMG30, off-road wheels with diameter
11 cm. The heart of the robot is a powerful DSP BF537, which provides 1000 MIPS
computational power. There is 32 MB RAM available, 4 MB Flash, camera OV9655, 3
sonars SFR08, GPS LEA-5H, AHRS VN 100, secondary 3-axis compass and
accelerometer. The control of motors is managed by two MD25 units. The communication
with the external world is by WiFi, OLED touch display and piezo speaker. The
energy source is 10 NiMH batteries pack with 4.5 Ah capacity. The robot is equipped with
a holder for 5l beer barrel.
The control program for the robot is written in C language and some time critical routines in
assebler. The road detection is computed from histogram
segmentation in HSV color space of grabbed image. The control algorithm tries to keep robot in
the middle of the road. The objects with different colors are not
considered to be road and this automatically leads to an obstacle avoidance. Sonar is
also used for the obstacle detection, its avoidance and stop in case of emergency.
Readings from encoders, AHRS and GPS are used for robot position location and
orientation.
Eduro
The winners of Robotour 2010. There are almost no hardware changes of the robot
since the last year. Learning from past mistakes, we replaced the
two-dimensional magnetic compass with a three-dimensional one. Other sensors
remain untouched: Odometry, lidar (SICK LMS100), sonar (not used), 1Hz GPS and
an IP camera with a fish-eye lens. The ALIX single-board computer takes care of
all computations. If we need more computational power, we have Gumstix Overo
Fire boards ready to take over part of the work. We are getting the software
where we wanted it last year. There is a big chance we break it doing this
We focus on road recognition and obstacle avoidance. We may even use the GPS
information this year. However, who would bother, whent it is better without
it? (JI)
Radioklub Písek
What's new in Radioklub Pisek? „We had to modify the robot due to the rules
change - there is a new holder of beer barrel and the construction is firmer now.
The robot is lighter by one piece of battery and we improved connectors for
easier and faster battery exchange. The H-bridges are modified and we are working on
a new motor controller. We also work on new software, so there is still what to
do, and we hope we will manage everything all in time to our satisfaction.”
Roboauto Karlík
Karlik is modified toy car for kids PegPerego with modified accelerator
controller from MAN truck. Smooth speed control forward and backward, LIDAR
sensor for the obstacle detection, inertial unit, GPS, ultrasound detector in
front, magnetic compass, Sony camera. The power source is 12V battery from car.
Computational power is based on two notebooks Hewlett Packard + 100 MBit switch.
SICK LIDAR + ultrasound + camera are used for obstacle avoidance. Software is
all home made, based on Windows platform, combination of applications in C++,
Delphi and Java. The intercommunication is via TCPIP.
Roboauto Quido
Quido is modified car hobby model. Implemented is smooth speed control forward
and backward. There are 3x LIDAR sensors for obstacle detection, inertial unit, GPS,
magnetic compass and camera.
The software is written in C++, Delphi a Java. It runs on Windows OS and it
communicates via TCPIP.
Short Circuits Prague
The robot is based on platform from 1:5 model of monster truck. The main
computational power is standard notebook. The hardware is monitored via Arduino
Duemilanove board. The robot's sensor set consists of magnetic quadrature
encoder, compass, sonars, GPS receiver and camera. Software is written in
Python language. The program collects current information about HW status via
USB. This information is gathered by microchip ATMEGA328, and regularly sent
as a data packet to the main computer. The main program ensures status
transformation (independently on HW platform), PID regulator of speed,
localisation from odometry, GPS and compass, obstacle detection with
corresponding actions and finally navigation on entered trajectory. The robot
recognizes road from camera images and detects obstacles with sonars.
Information from both sensors integrated into local map and with Vector Field
Histogram algorithm plans next step.
Smely Zajko
At the moment we are only a step forward. We managed to get working new
compass, tested various types of neural networks, improved formulas for robot
vision, and it is driving more or less fine. There is still plenty of space for
testing and further improvement …
Newbies
There are several new teams, but their information is quite incomplete. There
is typically still a lot of work on robotic platform so mostly even photo of
the robot is missing now. Hopefully that will change soon.
[FAIL]
[FAIL] is an Austrian team. The route decryption will happen on a notebook and
the basic controls will be handled by a microcontroller (likely an ATMEGAXXX,
32bit are also possible though) The chassis will most likely be based on a
track vehicle The Sensors will use both, optical and ultrasonic principles for
obstacle detection. If there is time left, obstacle avoidance could very well
be possible. Part of the Software is going to be written in C++ and maybe also
Basic, the Controller Firmware in C.
4Future
Team from Poland, experienced participants from Robot Challenge.
B-Team
Slovak team, with a custom built robot base with mostly custom built
electronics. Robot is controlled by a netbook. The robot will use ultrasonic
range finder for obstacle detection. Software is based on ROS with custom code
running under Linux.
HACKERSPACE PISEC
This is spin-off of Radioklub Písek team. This team will compete with four
wheel drive base Dřevo from RK Písek and it will try to avoid obstacles with
sonar.
KART
Austrian team from Fh Technikum Vienna: Our roboter design is based on the
Pioneer 3-AT. Apart from the 16 ultra sonic sensors which a pre build in, we have
added a i5 quad core to do all the main work. Sensors wise we have added a
bumblebee stereo camera, a laser, an odometrical unit and gps. The programming
was done under Linux and is based on ros as well as self coded routines.
MoonRabbit
Slovak team based in Bratislava.
Team members are mostly software engieneer and theoretic robotic who finally
decided to build their own robot. Because of the mostly software background the
focus will be mostly on control software, architecture, extendability and
robustness.
The robot name is "Spirit j.r." ( i.e. Junior), and it is 6 wheels robot based
on 1:8 rock crawler, 3 cameras, Kinect, 4 ultrasound sensors, compass and
GPS.
RoboTeam
New Czech team, which built robot on Audi TT hobby model platform.
HARDWARE:
- EEE_PC 901
- camera Sony DCR-TRV33E
- GPS Garmin Etrex Venture HC
- control modul from robot Mark III
- magnetic compass
For obstacle detection we will use IR Sharp rangefinder and ultrasound sensor.
The code is written in C# and in C.
The Experts
The team from Slovenia FERI Maribor and ERŠ Ptuj. For basic platform we built a
robotic platform in shape of the tank, which is universal and will also be used
in other projects. For purpose of this competition we mounted portable
computer, SICK 2D laser rangefinder, camera and GPS on the top of the robotic
platform. On the computer we are running software partly written in Visual C#
which is taking all the decisions and controlling the robot and partly in
Matlab for video recognition. All the other electronics is mounted in robotic
platform.
If you want this contest somehow support or you have some comments/questions,
do not hesitate to contact us via web
form.